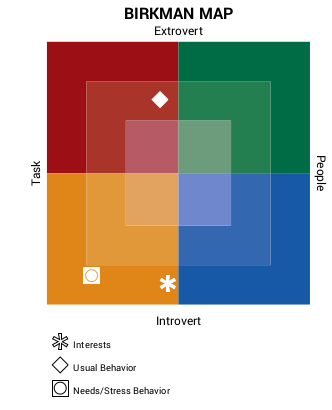
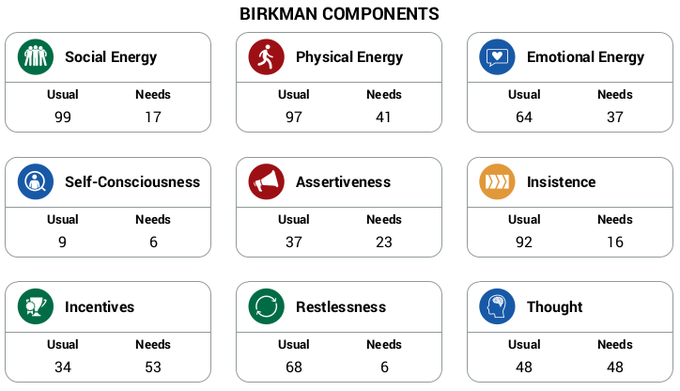
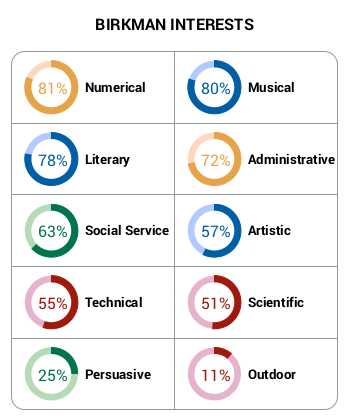
First, install docker and docker-compose in both VMs.
You may also need to add the user to docker group
$ sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
and either log out and log in again (or restart, in case of a VM).
VM1:
Install Keycloak with Docker, together with a user accountFirst, create a fullchain.pem and privkey.pem from Letsencrypt.
Step 1: Keys!
Two options.Option 1: Copy and rename the crt and key
$ cp keys-keycloak/fullchain.pem https/tls.crt
$ cp keys-keycloak/privkey.pem https/tls.key
Option 2: Create the crt and key with OpenSSL.
Alternatively, the crt and key can be created as below.
$ openssl x509 -outform der -in fullchain.pem -out tls.crt
$ openssl rsa -in privkey.pem -out tls.key
Move the tls.crt and tls.key to a separate folder (https) and cd to that directory.
Step 2. Set the permissions for the keys
$ cd https
$ chmod 700 .
$ chmod 600 tls.key
$ chmod 644 tls.crt
Step 3. Run the Keycloak container
$ docker run -d -p 443:8443 -e KEYCLOAK_USER=pradeeban -e KEYCLOAK_PASSWORD=password -v /home/pradeeban/https:/etc/x509/https --name kc jboss/keycloak
Now go to https://HOSTNAME
Log in with the user name and password you specified before.
Step 4. Now to configure a log in connect for Kheops
First create a new realm with the name, "demo".
1. Keycloak KHEOPS Login Client
Click the "Clients" tab, and choose the "Create" option.
Client ID = loginConnect
Click "Save", which will then open more configurations for the "LoginConnect" that you just created.
Turn on the option "Implicit Flow Enabled"
Turn off the "Direct Access Grants Enabled"
Valid Redirect URIs: https://KHEOPS-HOME/*
(for example: https://dbmi.virtualpacs.org/*)
Web origin: https://KHEOPS-HOME
(for example: https://dbmi.virtualpacs.org)
Click "Save" again.
2. Client Scope (kheops)
Click the "Client Scopes" tab, and choose the "Create" option.
Name: kheops
Turn off the "Display On Consent Screen"
Click "Save"
Click "Clients" again and go to "LoginConnect"
Go to the "Client Scopes" tab.
Choose "kheops" from the Available Client Scopes and choose the "Add selected" option. Remove all the other options from the Assigned Default Client Scopes as well as Assigned Default Client Scopes.
Add the email and full name token mappers to the kheops Client Scope by clicking on the Add Builtin button.
3. Service Account
Create another client "kheopsAuthorization".
Save, and then disable "Standard Flow Enabled" and "Direct Access Grants Enabled".
Change "Access Type" to "Confidential". and save.
Change "Service Accounts Enabled" to "On" and save.
The Service Account’s credentials (secret) can be found under the Credentials tab.
Choose the "KheopsAuthorization" Scope mappings. Under the "scope", disable "Full Scope Allowed" option. Choose "realm-management" as the "Client Roles", and add "view-users" option.
Now, repeat the above step for "Service Account".
The Service Account’s credentials (secret) can be found under the Credentials tab. Copy it to replace the default secret provided in kheopsDocker/kheops/secrets/kheops_keycloak_clientsecret, or provide it as the secret when prompted during the Kheops configuration.
4. Logging Impersonations
Under the "LoginConnect" client's Mappers tab, click "Add Bulletin", and add the Impersonator User ID."
Change the "Token Claim Name" to "act.sub". Then disable "Add to ID token" option.
Finally, click "Save". This is supposed to conclude the configurations unless I missed something.
Export your realm for later use from the host:
$ docker exec -it kc /opt/jboss/keycloak/bin/standalone.sh -Dkeycloak.migration.action=export -Dkeycloak.migration.provider=singleFile-Djboss.http.port=8888 -Djboss.https.port=9999 -Djboss.management.http.port=7777-Dkeycloak.migration.file=kkconf.json
Copy the file to the host machine, from the Docker container.
$ docker cp kc:/kkconf.json .At the time of writing, Keycloak documentation had some issues that are fixed in the above command. Then next time, you can easily import this realm, rather than configuring everything from scratch: $ docker run -e KEYCLOAK_USER=USERNAME -e KEYCLOAK_PASSWORD=PASSWORD \
-e KEYCLOAK_IMPORT=/tmp/example-realm.json -v /tmp/example-realm.json:/tmp/example-realm.json jboss/keycloak
Step 5: Configure Kheops
VM2:
Run Kheops with Docker
$ git clone https://github.com/OsiriX-Foundation/kheopsDocker.git
$ cd kheopsDocker
$ git checkout install-secure
$ sh kheopsinstall.sh [See footnote at the end of this post].
Follow the prompts.
Enter the secret: Enter the secret copied from Keycloak in the previous step.
What is the Keycloak host ? (ex: https://keycloak.kheops.online) https://keycloak.virtualpacs.org
What is the Keycloak realm ? demo
What is your hostname ? (ex: demo.kheops.online) dbmi.virtualpacs.org
Add your public and private key in the directory kheops/secrets (fullchain1.pem / privkey1.pem)
$ cp keys-kheops/fullchain.pem kheopsDocker/kheops/secrets/fullchain1.pem
$ cp keys-kheops/privkey.pem kheopsDocker/kheops/secrets/privkey1.pem
Press enter to start KHEOPS
Now, access Kheops from https://dbmi.virtualpacs.org
To enable registrations of new users for Kheops, go to Realm Settings -> Login tab in your Keycloak instance and turn on User registration. If you do not want to allow anyone to create an account, you may instead click on Users -> Add user to manually create users.
Feb 19, 2020: As of today, there is a minor tweak needed for this to get working.
In the .env file, set:
KHEOPS_REVERSE_PROXY_IMAGE_TAG=v0.9.0-contentsecurity-fixbefore running the kheopsinstall.sh.